Recent News
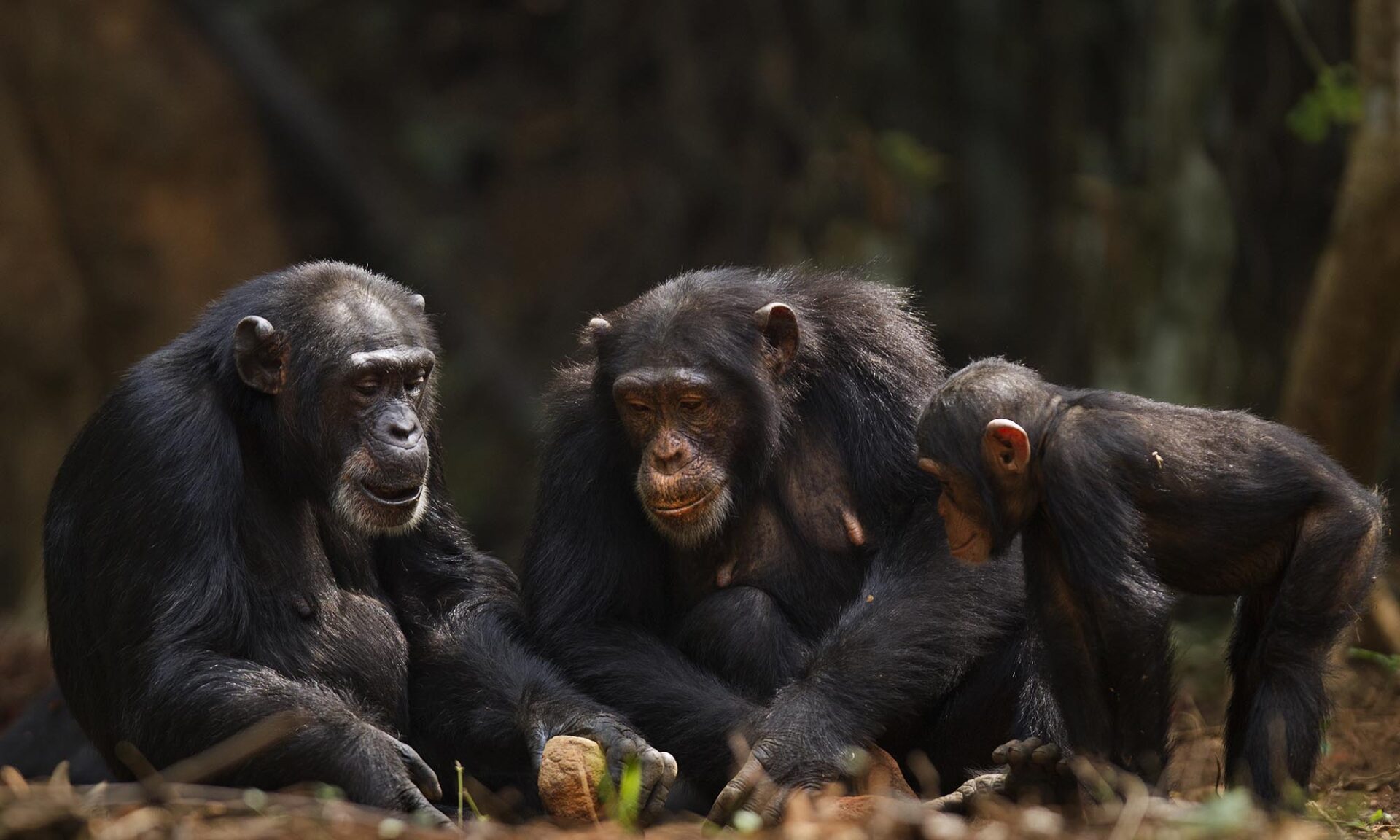

Wild chimpanzees show human-like cognitive decline with age
For decades, scientists assumed only humans experienced dementia. Now, new field observations suggest that wild chimpanzees—our closest primate relatives—may also show signs of cognitive decline with age.

Faculty Q&A: Elise Piazza, PhD
Elise Piazza, PhD, is an assistant professor of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Neuroscience at the University of Rochester. She completed her undergraduate degree in Cognitive Science and Music at Williams College, her PhD at the University of California, Berkeley, and her postdoctoral training as a C. V. Starr Fellow at the Princeton Neuroscience Institute. Today, her research aims to understand how the brain organizes natural sounds, including speech and music, and how multiple people’s brains and behaviors align to support interpersonal communication.

University scholars shine in Fulbright program
Congratulations to the recent UR recipients of the Fulbright US Student program, including two School of Arts and Sciences alumni. Isabelle Miranda ’23 BS, BA (neuroscience and gender, sexuality, and women’s studies) earned a Fulbright grant for an English Teaching Assistantship in Taiwan. Daniel Pyskaty ’25 BS, BA (brain and cognitive sciences and linguistics) earned a Fulbright grant to conduct research at the Institute of German Linguistics at Philipps Universität Marburg.
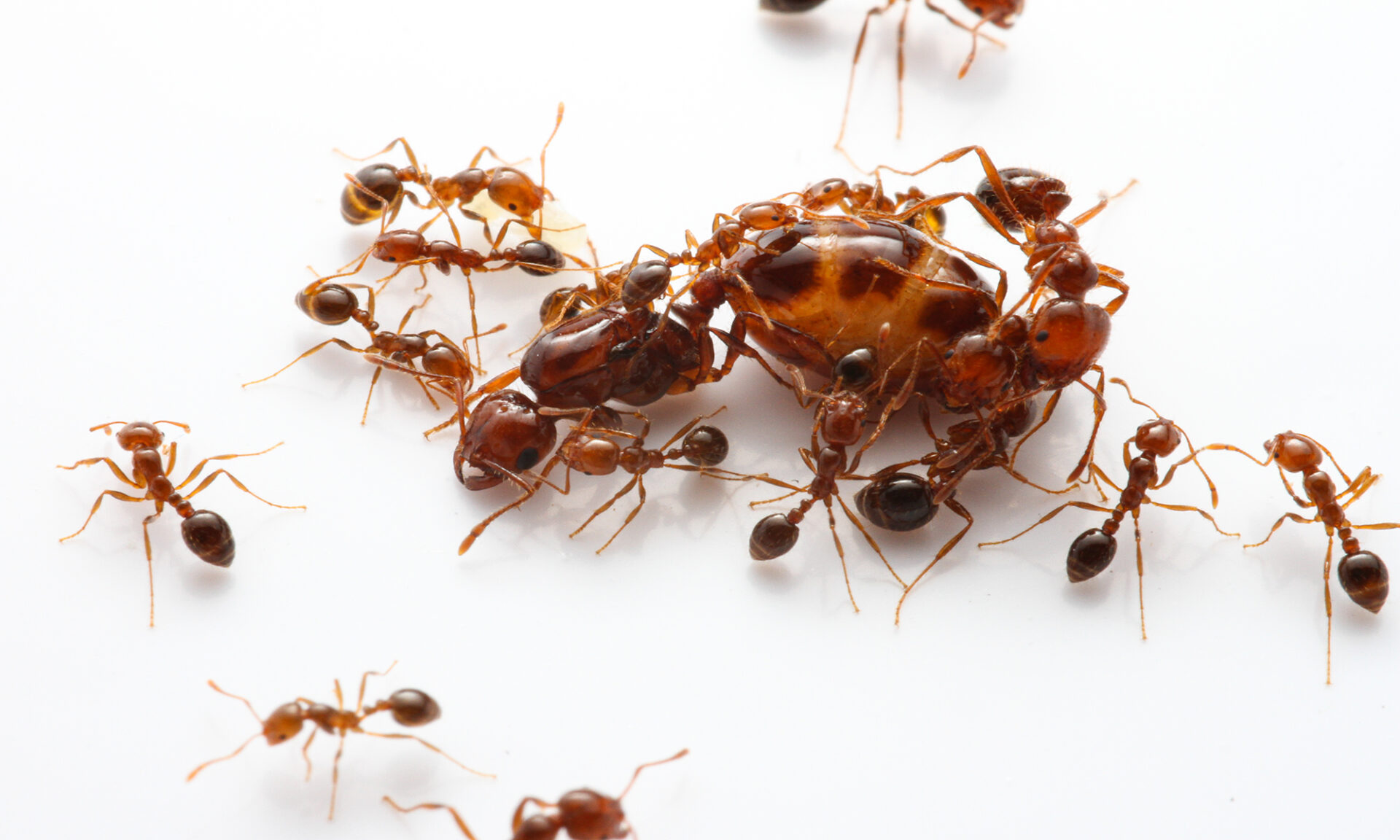

How the genetic few can sway the many
In a paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), researchers studied minority influence in fire ants—highly social insects—and discovered a surprising genetic underpinning to the phenomenon. The research offers insights into how social interactions shape individuals and groups.“Our research may help us understand how other animals make consensus decisions,” says Takao Sasaki, an associate professor in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at the University of Rochester.

Student Spotlight: Yue Guzhang
Yue Guzhang is a fourth-year student in the Brain and Cognitive Sciences (BCS) Program at the University of Rochester. She received her undergraduate degree in BCS from the University. Guzhang works with Associate Professor Martina Poletti, PhD, in the Active Perception Lab, studying how attention and fixational eye movements influence our ability to see fine details in the fovea.
How artificial general intelligence could learn like a human
Turns out, training artificial intelligence systems is not unlike raising a child. That’s why some AI researchers have begun mimicking the way children naturally acquire knowledge and learn about the world around them—through exploration, curiosity, gradual learning, and positive reinforcement.

Sculpting the brain (without chisel or scalpel)
Imagine being able to inscribe a new pattern of activity into a person’s brain that would allow for faster learning, or better treatment of psychiatric and developmental disorders such as depression or autism. Now imagine being able to do that in a way that doesn’t require brain surgery or any physical manipulation. Sounds like science fiction?

Turning brain cells on using the power of light
University of Rochester researchers have demonstrated a noninvasive method using BL-OG, or bioluminescent optogenetics, that harnesses light to activate neurons in the brain. The ability to regulate brain activation could transform invasive procedures such as deep brain stimulation that are used to treat Parkinson’s disease and other neurological conditions.

Why teens with autism struggle with speech intonation
A new study reveals that difficulties in adapting to changes in speech patterns may affect how adolescents with autism understand tone and meaning.

Sparks Picked by the Cardinals in the 2024 MLB Draft
University of Rochester Neuroscience major and right-hander Nolan Sparks was selected by the St. Louis Cardinals with the 381st pick in the 13th round of the 2024 Major League Baseball (MLB) Draft.

Tadin named interim dean of the School of Arts & Sciences
Duje Tadin, chair of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences (BCS), has been named interim dean of the School of Arts & Sciences. In this role—a position he also held in summer 2023, just before Nicole Sampson began as dean—Tadin will assume oversight of the school’s 19 departments and numerous centers, institutes, and programs in the arts, humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.

Why do we blink so much?
Researchers find that blinking plays a pivotal role in processing visual information—adding to a growing body of evidence revising our conventional views of vision.

Yue Guzhang receives 2024 Edward Peck Curtis Award for Excellence in Teaching
The Edward Peck Curtis Awards for graduate student teaching are given to a small number of full-time graduate students who have a role in undergraduate education. Recipients have assisted in undergraduate instruction, and have had significant face-to-face interaction with undergraduates in the classroom or laboratory.

Announcing Dora Biro as the VSS 2024 Keynote Speaker
VSS is pleased to welcome Dora Biro as the VSS 2024 Keynote Speaker.
URMC Selected for NIH Initiative to Map Connections in the Brain
Scientists at the University of Rochester Medical Center are joining research teams across the globe to develop next-generation tools for visualizing connections in the human brain. Imaging and understanding the brain’s intricate circuitry at the cellular and microscopic level will advance new approaches to treat brain disorders like Tourette’s syndrome, Parkinson’s disease, and obsessive-compulsive disorder.

Does what we see impact our brain function?
Duje Tadin, PhD, chair of the Brain and Cognitive Sciences Department at the University of Rochester studies this to understand how visual perception differs in conditions like autism, stroke, and schizophrenia.

Pathway program proves access can cultivate scientists
In the summer of 2021, the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience Diversity Commission and the City College of New York launched the partnership program NEUROCITY. Using the Summer Scholars Program at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry as a model, organizers created a program that has, to date, put nearly 30 undergraduate students from historically marginalized backgrounds in research labs across the University of Rochester and University of Rochester Medical Center campuses.

Research finds prediction may be key to eye-and-hand coordination
Have you ever made a great catch—like saving a phone from dropping into a toilet or catching an indoor cat from running outside? Those skills—the ability to grab a moving object—takes precise interactions within and between our visual and motor systems. Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester have found that the ability to visually predict movement may be an important part of the ability to make a great catch—or grab a moving object.

Small, involuntary eye movements help us see a stable world
Scientists have long sought to understand how we humans can perceive the world as stable as our eyes are constantly moving. Past research has suggested that, in the intervals between voluntary gaze shifts, the human visual system builds a picture of a stable world by relying solely on sensory inputs from fixational eye movements. According to new research by a team at the University of Rochester, however, there may be another contributing factor.

Seed funding reflects how data science, AR/VR transform research at Rochester
Ten projects supported with seed funding from the Goergen Institute for Data Science this year demonstrate how machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) are transforming the way University of Rochester researchers—across all disciplines—address challenging problems.

Brain’s cognitive bias dominates in fantasy sports
Renee Miller has participated in fantasy football since 2006. But it wasn’t until the fall of 2012 that Miller, a professor of brain and cognitive sciences at the University of Rochester, realized she could combine her expertise in neuroscience with her love of fantasy sports.

What Babies Hear When You Sing to Them
From The Atlantic: “Babies are pattern detectors,” says Elise Piazza, a University of Rochester professor who has studied early-childhood communication through language and music. Piazza told me that singing creates a feedback loop, where a baby’s enjoyment motivates parents to sing more and builds parents’ confidence.

CAREER awards recognize role models in research, education
Six Rochester researchers, including BCS professor Ralf Haefner, have received prestigious NSF awards for early-career faculty members. The awards, NSF’s most esteemed recognition for early-career faculty members, provide recipients with five years of funding to help lay the foundation for their future research.

Sensory processing—in a virtual Kodak Hall
A cross-disciplinary team of researchers from the University of Rochester is collaborating on a project to use virtual reality (VR) to study how humans combine and process light and sound. The first project will be a study of multisensory integration in autism, motivated by prior work showing that children with autism have atypical multisensory processing.

How the brain interprets motion while in motion
In a new paper published in the journal eLife, researchers at the University of Rochester, including Greg DeAngelis, the George Eastman Professor of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, and his colleagues at Sungkyunkwan University and New York University, describe a novel neural mechanism involved in causal inference that helps the brain detect object motion during self-motion.

Diverse minds and determined hearts make change: Forging equitability in Neuroscience
A group, mostly consisting of neuroscientists, meets bi-weekly outside the lab with a simple but powerful common purpose – to fundamentally change the bench.
Emily Isenstein receives pre-doctoral fellowship from Autism Science Foundation
The Autism Science Foundation (ASF), a nonprofit organization dedicated to funding innovative autism research and supporting families facing autism, today announced the recipients of its annual pre- and postdoctoral fellowship grants. BCS graduate student Emily Isenstein is among the recipients.

Dora Biro among eight faculty members appointed to named professorships
Dora Biro, a professor of brain and cognitive sciences, has been jointly appointed as the Beverly Petterson Bishop and Charles W. Bishop Professor of Brain and Cognitive Sciences.

Why some misremembering might show your memory is functioning properly
From The Washington Post
When asked the other day about a bakery near my home, I responded that I’d recently eaten its mouthwatering chocolate chip cookies. My wife corrected me, noting that the cookies I ate were actually oatmeal raisin. Why did I make this memory error?

Brief period of ‘blindness’ is essential for vision
In a new paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers at the University of Rochester, including Michele Rucci, a professor of brain and cognitive sciences, and Janis Intoy, a postdoctoral research associate in Rucci’s lab, further cement the evidence for the important role of these tiny movements.

Curtis Award spotlights PhD teaching assistants’ ‘amazing’ efforts during the pandemic
The four University of Rochester recipients of this year’s Edward Peck Curtis Award for Excellence in Teaching by a Graduate Student come from different disciplines. But they have several things in common.

Lab access: Diversifying the bench
“Science is nature’s art,” Mariana Espinosa-Polanco said. The art and psychiatry major is a rising senior at The City College New York (CCNY) and one of the eight scholars in the inaugural class of NEUROCITY. “I graduate in December and plan to continue to pursue science because of this experience.”

New program puts students from CCNY in neuroscience labs this summer
The Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience Diversity Commission (NDC) is working to create a pipeline for underrepresented minorities interested in pursuing neuroscience research. Eight undergraduate students from City College of New York (CCNY) are living and working at the University of Rochester this summer as part of a new program called NEUROCITY. NEUROCITY is a partnership between the University and City College New York.

Pipeline program lets East High students experience life in the lab
Lulu Abdullahi (right), a junior at East High School in the Rochester City School District, practices soldering to repair an experiment component with Manuel Gomez-Ramirez, an assistant professor in the University’s Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences. For six weeks, Abdullahi and a classmate visited the River Campus as part of NeURo East, a Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience program that gives underrepresented high school students access to scientific research experiences in an academic setting. In the fall, the program will expand to six students who will rotate through multiple Rochester labs during the academic year.

Martina Poletti has been awarded the James P. Wilmot Distinguished Assistant Professorship
Four University faculty members, including Martina Poletti, representing “some of the most promising young men and women in the early stages of their academic careers,” have been awarded James P. Wilmot Distinguished Assistant Professorships at the University of Rochester.

Research Funded to Study Efficacy of Early Visual Training after Occipital Stroke
Up to half-a-million people each year suffer occipital strokes that cause loss to some portion of their vision, permanently affecting how they navigate through life.

Congratulations to Martina Poletti, Recipient of the 2021 Elsevier/VSS Young Investigator Award
VSS is pleased to present the 2021 Young Investigator Award to Martina Poletti. Dr. Poletti is an assistant professor in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at the University of Rochester. She is recognized for fundamental contributions to our understanding of eye movements, microsaccades, and the nature of visual-motor function and attention within the foveola. She received her Bachelor’s degree and Master’s degree at the University of Padova, and completed her doctoral and postdoctoral work at Boston University.

More than words: Using AI to map how the brain understands sentences
Have you ever wondered why you are able to hear a sentence and understand its meaning – given that the same words in a different order would have an entirely different meaning? New research involving neuroimaging and A.I., describes the complex network within the brain that comprehends the meaning of a spoken sentence.

Rochester brain and cognitive sciences researchers receive national recognition
Two University of Rochester researchers in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences are being honored with a celebrated award for their contributions to and leadership in the scientific community.

Rochester leads novel research project on how the brain interprets motion
Major NIH award to study how the brain infers structure from sensory signals may have applications for disorders like schizophrenia and offer insights for artificial intelligence.

Study: Neurons can shift how they process information about motion
New Rochester research indicates some neurons may be more adept than previously thought in helping you perceive the motion of objects while you move through the world.

‘Time is vision’ after a stroke
A person who has a stroke that causes vision loss is often told there is nothing they can do to improve or regain the vision they have lost.

Rochester scientist earns national recognition for research
University of Rochester faculty member Adam Snyder has been named one of this year’s recipients of a Sloan Research Fellowship, a national recognition awarded to young scientists considered to be potential future leaders in the scientific community.

Q & A with Adam Snyder, Ph.D.
Adam Snyder, Ph.D., joined the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience in July 2018 as an assistant professor in Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Neuroscience, and the Center for Visual Science. He received his B.A. in Language and Mind from New York University and went on to complete his Ph.D. in Cognitive Neuroscience from the City College of New York. His research focuses primarily on vision, visual attention and memory.

Adam Snyder named a 2020 Sloan Research Fellow
The Alfred P. Sloan Foundation is pleased to announce the selection of 126 extraordinary early career researchers as recipients of the 2020 Sloan Research Fellowships. Awarded annually since 1955, the fellowships honor scholars in the U.S. and Canada whose creativity, leadership, and independent research achievements make them some of the most promising researchers working today.

Small eye movements are critical for 20/20 vision
Researchers previously assumed that visual acuity was primarily determined by the optics of the eye and the anatomy of the retina. Now, researchers from the University of Rochester—including Michele Rucci, a professor of brain and cognitive sciences, and Janis Intoy, a neuroscience graduate student at Boston University and a research assistant in Rucci’s lab in Rochester—show that small eye movements humans aren’t even aware of making play a large role in humans’ visual acuity. The research, published in the journal Nature Communications, may lead to improved treatments and therapies for vision impairments.
Q&A with Farran Briggs, Ph.D.
Farran Briggs, Ph.D., joined the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience in 2017 as an associate professor in the Departments of Neuroscience, Brain and Cognitive Sciences, and the Center for Visual Sciences. She received her B.A. in Biology from Dartmouth College and Ph.D. in Biology from the University of California, San Diego. Her work focuses on neuronal circuits in the visual system, and how attention affects the brain’s ability to process visual information.

Making a study of adapting to change
When Karl Rosengren’s oldest daughter was a toddler, he and his wife—Rochester’s new president, Sarah C. Mangelsdorf —observed her attempting to get into a doll-sized toy car that was no bigger than her foot.

New training in AR/VR tech gives Rochester doctoral students an edge
A $1.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation will provide additional impetus to a University of Rochester initiative applying augmented and virtual reality in health, education, product design, remote communication, entertainment, and other fields.

Q&A with Manuel Gomez-Ramirez, Ph.D.
This summer, Manuel Gomez-Ramirez arrived from Brown University to join the University of Rochester (UR) as an assistant professor in the Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences (BCS) and Neuroscience. His Haptic Perception Lab will focus on developing mechanistic models of how objects are perceived and manipulated with our hands, with the ultimate goal of using these models to optimize neural stimulation strategies for brain-computer interfaces and neuroprosthetics. We sat down with Manny, the guitar-playing, cocktail-making neuroscientist, to talk about what he’s most looking forward to at UR.

Why can we see moving objects against their backgrounds?
According to new research from scientists at the University of Rochester, one reason human beings are good at discerning smaller moving objects in the foreground is that the brain becomes desensitized to the motion in the larger background. Conversely, when a person’s brain is more sensitive to background motion, the negative trade-off is that she will be less sensitive to smaller foreground objects. The research, published in the journal Nature Communications, could lead to new training programs for elderly adults and patients with conditions such as schizophrenia, which has been linked to weaker motion segregation.

Brain stimulation helps patients with vision loss re-learn how to see
Practice results in better learning. Consider learning a musical instrument, for example: the more one practices, the better one will be able to learn to play. The same holds true for cognition and visual perception: with practice, a person can learn to see better—and this is the case for both healthy adults and patients who experience vision loss because of a traumatic brain injury or stroke.

2019 BCS University Research Award Winners
Congratulations to Farran Briggs, Jude Mitchell, and Michele Rucci, who were all 2019 recipients of University Research Awards (URA). Originally called Provost’s Multidisciplinary Awards, the University Research Awards (URA) provide "seed" grants for promising, high-risk projects, says Robert Clark, provost and senior vice president for research.

Two degrees for a student with music on her mind
Hannah Dick ’19, ’19E knew she wanted to pursue a college degree in music. But that wasn’t all. Graduating with dual degrees in percussion and brain and cognitive science, she plans to use music to help people.

All the info our brain needs for language nearly fits on a floppy disc
From New Scientist: As you learn your first language, your brain stores about 1.5 megabytes of information just a little over the amount that would fill a floppy disc (that is what the picture for the save icon represents, if you are too young to remember them).

Microscopic eye movements affect how we see contrast
It is often difficult for a driver to see a person walking on the side of the road at night—especially if the person is wearing dark colors. One of the factors causing this difficulty is a decrease in contrast, making it hard to segment an object, such as a person, from its background.

The science of seeing art and color
During three trips to London at the turn of the 20th century, Claude Monet painted more than 40 versions of a single scene: the Waterloo Bridge over the Thames River. Monet’s main subject was not the bridge itself, however; he was most captivated by the landscape and atmosphere of the scene, with its transitory light, fog, and mist.

Attention Requires Balance in the Brain
The ability to focus attention is a fundamental challenge that the brain must solve and one that is essential to navigating our daily lives. In developmental disorders such as Autism this ability is impaired. New research published in the journal Nature Communications shows that nerve cells maintain a state of balance when preparing to interpret what we see and this may explain why the healthy brain can block out distractions.

Professor recognized for transforming understanding of human language
Michael K. Tanenhaus, a longtime professor of brain and cognitive sciences, is being recognized for work that has “transformed our understanding of human language and its relation to perception, action, and communication” by the premier academic society in his field.

‘Groundbreaking and transformative’ work at Undergraduate Research Expo
A diversity of subject matter was on display this year at the University of Rochester’s annual Undergraduate Research Exposition. Students presented projects in topics ranging from fluid dynamics, deforestation in Bolivia, and nomad cultures in Morocco to prenatal depression, meteorites, and software that affects education.

Professor studies complex brain networks involved in vision
Our brains are made up of an intricate network of neurons. Understanding the complex neuronal circuits—the connections of these neurons—is important in understanding how our brains process visual information.

A professor and his robot study how we see
Vision and art have always played a large role in Michele Rucci’s life.

Training brains—young and old, sick and healthy—with virtual reality
An accidental discovery by Rochester researchers in 2003 touched off a wave of research into the area of neuroplasticity in adults, or how the brain’s neural connections change throughout a person’s lifespan.
